Case Study: Starbucks Causes Global Jitters

Starbucks began its global expansion in 1996 with its first international store in Tokyo and now operates 24,000 retail stores across 70 countries. The company successfully brought European-style coffee to the United States before expanding its American-style coffeehouses to Europe, carefully researching markets before entry. In Switzerland, Starbucks used the multicultural environment to learn about conducting business throughout Europe.

The company later introduced coffee culture to China, where it plans to open 500 stores annually through 2021, targeting the enormous potential of the 1.4 billion population. After rebounding from challenging years, Starbucks renewed its focus on coffee while maintaining its “Shared Planet” commitment to social responsibility.
The chapter discusses how companies traditionally enter familiar, nearby markets first but now often analyze locations simultaneously as potential markets and operational sites, emphasizing the importance of high-quality market research to understand buyer behavior, business environments, and inform strategic decisions.
1. Introduction to International Market and Site Analysis
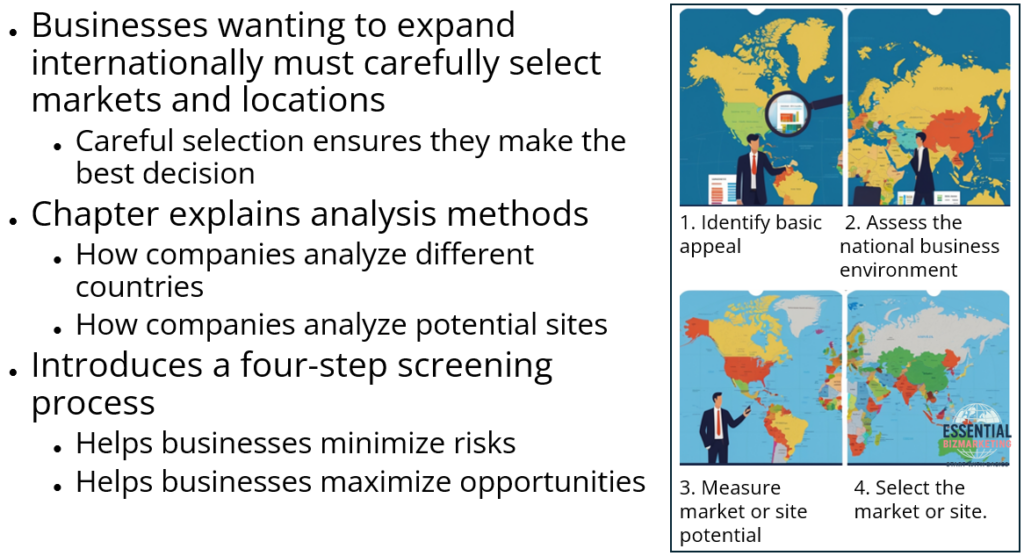
Businesses that want to expand internationally must carefully select the right markets and locations for their operations. This chapter explains how companies analyze different countries and sites to ensure they make the best decision. It introduces a four-step screening process that helps businesses minimize risks and maximize opportunities.
2. Understanding Market and Site Selection

Before entering a foreign market or setting up a business site, companies consider two key factors. The first factor is basic market demand. Companies must determine if there is a demand for their product in a particular country. If there is no demand, expansion to that market is not viable. The second factor is resource availability. Businesses need to check if essential resources like labor, raw materials, and financing are available in the selected country. For example, Starbucks researched the European and Chinese markets before expanding, ensuring there was enough demand for coffee.
3. The Four-Step Screening Process
Step 1: Identifying Basic Appeal

Before considering any market, businesses must check several factors. Climate suitability is essential because some products, such as winter coats, will not sell well in tropical countries. Government restrictions can also affect market entry. Some governments ban certain products, such as alcohol in Islamic countries. Another key consideration is the availability of resources. If a country lacks essential resources like skilled workers, it may not be a good location for production.
Step 2: Assessing the National Business Environment

Countries differ in their economic, political, legal, and cultural environments, which impact business success. Cultural differences influence product demand and consumer preferences. Government regulations can create challenges, as some governments require foreign companies to work with local partners. Economic and financial conditions, including inflation and exchange rate fluctuations, affect profitability. Transportation and logistics also play a role, since high transportation costs and poor infrastructure can make it expensive to do business.
Coca-Cola faced difficulties in China because its flavor reminded consumers of traditional herbal medicine. To succeed, it used marketing strategies that associated Coke with American culture.
Step 3: Measuring Market or Site Potential
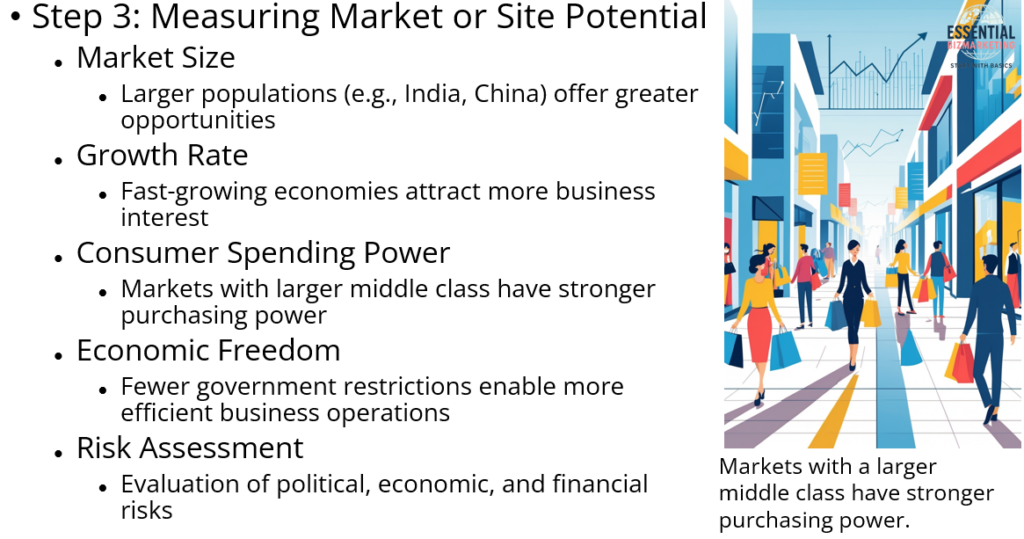
Once a market passes the first two steps, businesses analyze its economic potential. Market size is important because countries with large populations, such as India and China, offer bigger opportunities. Market growth rate is also a key factor, as fast-growing economies attract more businesses. Consumer spending power is another critical measure. Markets with a larger middle class have stronger purchasing power.
Economic freedom affects how easily businesses can operate in a country. Markets with fewer government restrictions allow businesses to function more efficiently. Finally, risk assessment is necessary to evaluate political, economic, and financial risks before entering a market. For example, companies prefer stable economies with strong infrastructure, like Germany or the United States, over unstable regions.
Step 4: Selecting the Best Market or Site

At this stage, businesses visit the potential markets to confirm their choices. Field trips help managers personally observe market conditions and meet local partners. Competitor analysis allows businesses to study their competition to understand pricing strategies, customer loyalty, and overall market dynamics.
4. Secondary Market Research

Secondary research involves collecting existing data from different sources. International organizations, such as the World Bank and International Monetary Fund, provide economic data. Government agencies offer reports on trade regulations and market conditions. Industry and trade associations publish market trends and industry reports. Service companies and consulting firms provide research on market demand and financial risks. The Internet is another useful resource, where companies can access online databases such as Google and LexisNexis to find market data.
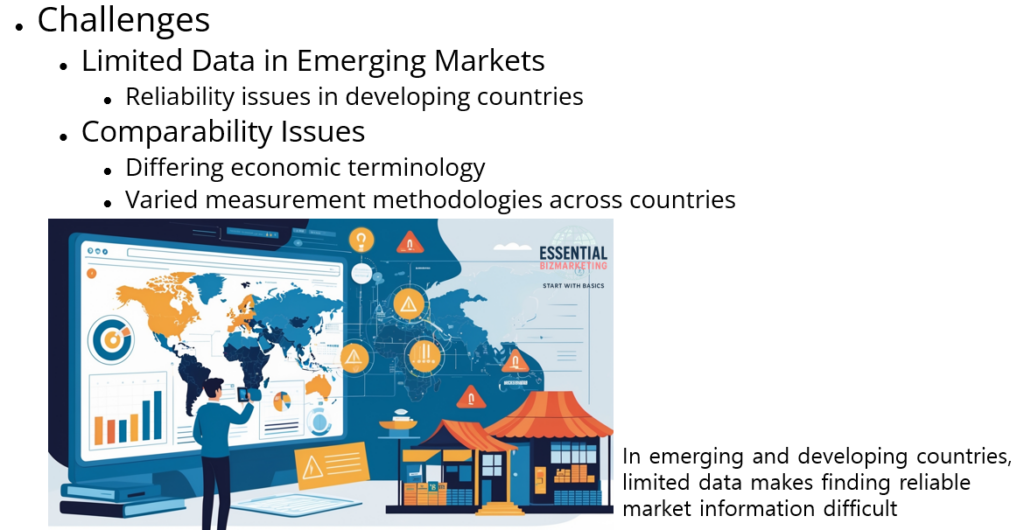
There are some challenges with secondary research. In many emerging and developing countries, data availability is limited, making it difficult for businesses to find reliable market information. Comparability issues can also arise because economic terms and measurement methods vary between countries.
5. Primary Market Research

If secondary data is insufficient, companies conduct their own research using various methods. Trade shows and trade missions help businesses showcase their products and meet potential partners. Interviews and focus groups allow businesses to interact directly with customers to understand their opinions and preferences. Surveys are another method, where businesses collect written or verbal responses from potential customers to assess market interest. Environmental scanning is an ongoing process that helps businesses monitor global trends to identify opportunities and risks.

Conducting primary research presents certain challenges. Cultural barriers, such as language differences and literacy rates, can make data collection difficult. In addition, primary research can be costly since it requires significant time and financial investment.
6. Conclusion
A structured approach to market research helps businesses make informed decisions. By following the four-step screening process, companies can identify the best international opportunities while minimizing risks. Understanding cultural, economic, and political factors is essential for successful global expansion.
Related videos
📚 References
Wild, J. J., & Wild, K. L. (2019). International business: The challenges of globalization (9th ed.). Pearson.
📁 Start exploring the Blog
📘 Or learn more About this site
🧵 Or follow along on X (Twitter)
🔎 Looking for sharp perspectives on global trade and markets?
I recommend @GONOGO_Korea as a resource I trust and regularly learn from.
