1. Key Economic Indicators for Bibigo Mandu’s International Expansion
CJ CheilJedang’s global expansion strategy for Bibigo Mandu must be guided by specific economic indicators that determine the feasibility and profitability of market entry. Several key metrics are crucial in assessing the potential of a foreign market.
The first critical factor is per capita income, which indicates consumer purchasing power. Higher per capita income suggests a greater likelihood of consumers being willing to purchase premium food products such as Bibigo Mandu. Countries with a higher income level are typically more open to premium and international brands.
The second factor is urbanization rate, which is essential in predicting the demand for processed and frozen foods. Countries with high urbanization tend to have a larger working-class population that prefers convenient and quick meal solutions, making Bibigo Mandu an attractive option.
The third consideration is the retail market size, as it determines the effectiveness of the distribution and availability of frozen food products. The presence of large supermarket chains and convenience stores enhances accessibility for consumers, facilitating the widespread sale of Bibigo Mandu.
Another critical factor is the food import dependency rate, which measures the extent to which a country relies on imported food products. Countries with a high import dependency are more likely to be receptive to international brands, making it easier for Bibigo to penetrate the market.
The cost of labor and production is another determinant for countries where Bibigo may establish manufacturing facilities. Lower labor costs make a country more attractive for local production, reducing costs and improving operational efficiency.
Lastly, the logistics and distribution infrastructure is essential, particularly for frozen food products that require cold-chain storage and transportation. A country with a well-developed logistics network enables efficient supply chain management, reducing product spoilage and enhancing distribution efficiency.
2. Comparative Analysis of Bibigo Mandu’s Target Markets Based on Economic Indicators
A comparative analysis of Bibigo Mandu’s international markets highlights key differences in economic conditions that influence its market strategy.
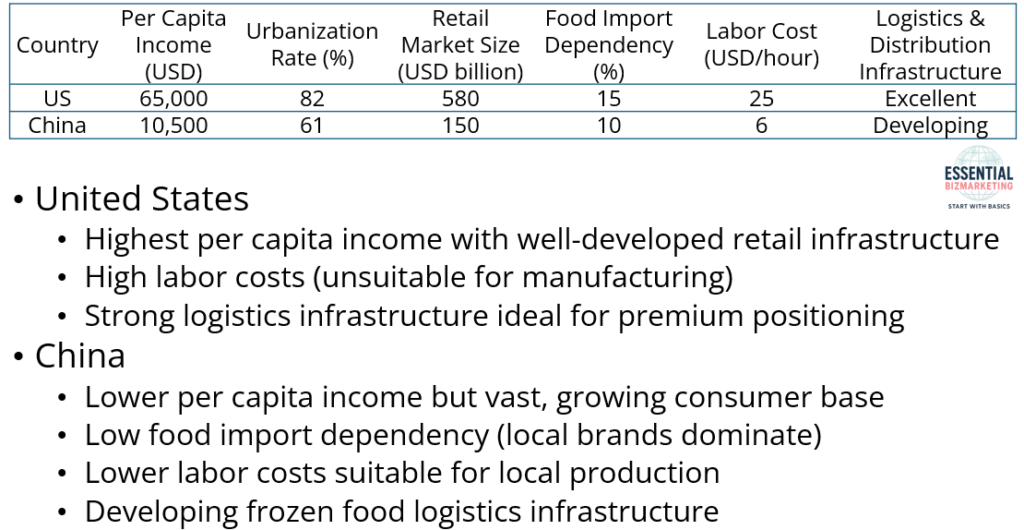
The United States has the highest per capita income, a well-developed retail infrastructure, and a strong urban population. However, labor costs are significantly high, making it unsuitable for manufacturing. Its well-developed logistics infrastructure makes it an ideal market for premium product positioning.
China, despite having a lower per capita income, has a vast and growing consumer base with an expanding retail market. However, its food import dependency is relatively low, meaning local brands dominate the market. The country’s lower labor costs make it suitable for local production, but logistics infrastructure for frozen food is still in development.
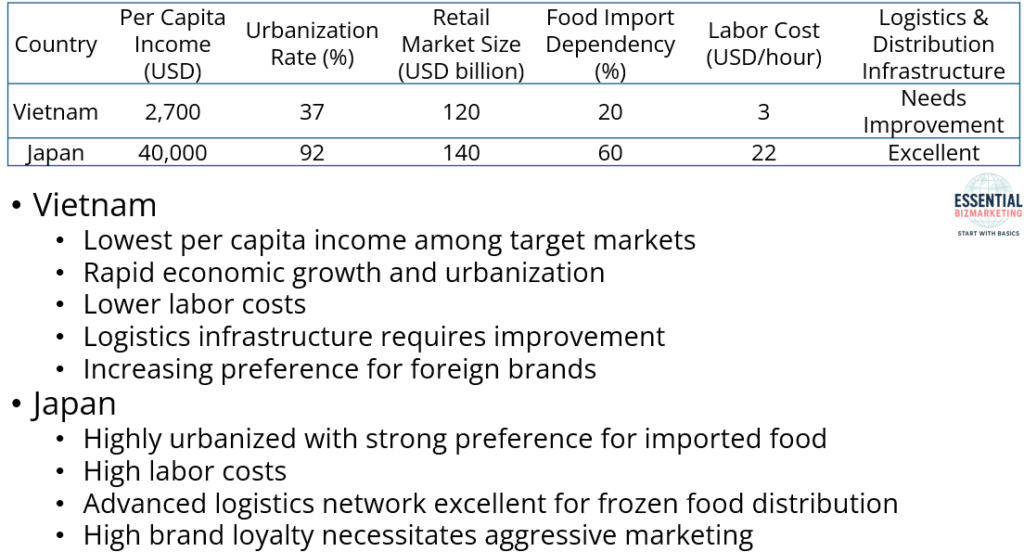
Vietnam has the lowest per capita income among the target markets but is experiencing rapid economic growth and urbanization. While its logistics infrastructure requires improvement, its lower labor costs and increasing preference for foreign brands provide a growth opportunity.
Japan is a highly urbanized country with a strong preference for imported food. Despite its high labor costs, its advanced logistics network makes it an excellent market for frozen food distribution. Its high brand loyalty suggests that aggressive marketing strategies are necessary to build consumer trust.
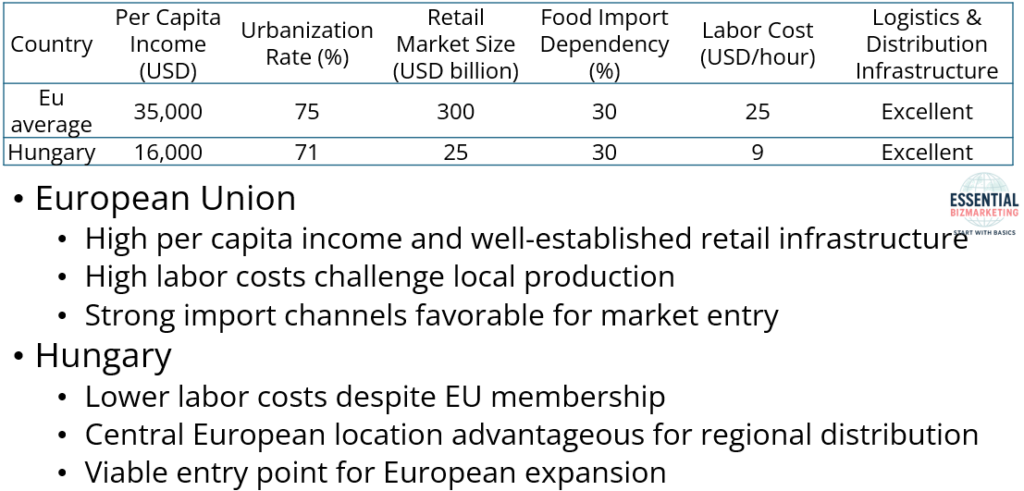
The European Union, as a whole, presents a diverse market with high per capita income and a well-established retail infrastructure. However, high labor costs make local production challenging. Bibigo’s penetration strategy in Europe depends on leveraging strong import channels and premium brand positioning.
Hungary, though part of the EU, presents a unique case due to its lower labor costs and central location within Europe. These factors make it an attractive site for regional production and distribution, reducing overall logistics costs. Hungary’s food import dependency rate aligns with the EU average, making it a viable entry point for Bibigo Mandu’s expansion.
3. Strategic Responses Based on the Comparative Analysis
The findings suggest that a differentiated strategy is required for each target market.

In the United States, Bibigo should maintain a premium brand strategy, focusing on large retail chains such as Costco, Walmart, and Amazon. Given the high labor costs, direct manufacturing in the U.S. is not feasible, making imports from production hubs like South Korea or Hungary more efficient.
In China, Bibigo must adopt a local production and affordability strategy to compete with domestic brands. Establishing partnerships with local retailers and emphasizing the authenticity of Korean cuisine will help differentiate Bibigo from competitors. Online platforms such as Alibaba and JD.com should be utilized for digital marketing and e-commerce sales.

In Vietnam, a value-driven market entry strategy is recommended, focusing on price competitiveness. Retail expansion in urban centers is crucial, and collaborations with local distribution partners will enhance market reach. Due to underdeveloped logistics, Bibigo should invest in supply chain infrastructure to support long-term growth.
In Japan, a premium and culturally adapted marketing strategy is necessary. Since Japanese consumers prioritize quality and brand trust, localized marketing campaigns emphasizing health benefits and unique flavors will be essential. Given the strong preference for imported products, Bibigo can position itself as a premium Korean offering through high-end supermarkets and specialty stores.

For the European Union, Bibigo should capitalize on import channels and premium branding, leveraging the strong demand for international cuisine. Since labor costs are high, imports from Hungary or South Korea should be prioritized. Hungary, as a strategic production hub, should be further developed to serve as a regional logistics center for Bibigo’s European expansion.
4. Conclusion

CJ CheilJedang’s global expansion strategy for Bibigo Mandu requires a tailored approach based on the economic conditions of each target country. The analysis of per capita income, urbanization rates, retail infrastructure, food import dependency, labor costs, and logistics capabilities provides a comprehensive understanding of each market’s potential.
The United States and Japan offer strong premium market opportunities, while China and Vietnam require localized production and affordability-focused strategies. The European Union, with Hungary as a production hub, presents opportunities for regional distribution efficiency.
By aligning market entry strategies with economic conditions, CJ CheilJedang can optimize Bibigo Mandu’s global market penetration, ensuring sustained growth and profitability in diverse international markets.
📚 References
Harvard Business Review. (2023). The global expansion of Korean food brands: The case of Bibigo Mandu. Retrieved from https://hbr.org
International Monetary Fund. (2024). World Economic Outlook Database. Retrieved from https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO
OECD. (2023). Retail market development in high-income countries. Retrieved from https://www.oecd.org
World Bank. (2024). Urbanization and economic growth trends in Asia and Europe. Retrieved from https://www.worldbank.org
Statista. (2024). Global frozen food market trends: Growth and consumer preferences. Retrieved from https://www.statista.com
📁 Start exploring the Blog
📘 Or learn more About this site
🧵 Or follow along on X (Twitter)
🔎 Looking for sharp perspectives on global trade and markets?
I recommend @GONOGO_Korea as a resource I trust and regularly learn from.
